C. VAISLIC, A. BENJELLOUN, J.-N. FABIANI, J.-F. BONNEVILLE, S. CHOCRON
Abstract
Current treatment of thoracoabdominal aneurysms is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The most feared and devastating complication is paraplegia accompanied by sphincter and posture problems. To try and reduce these complications we have treated patients with multilayer flow modulators which preserve collateral circulation and branch patency. The multilayer flow modulation concept offers a completely novel approach to thoracoabdominal aneurysm treatment. Aneurysms are excluded physiologically rather than mechanically while preserving vital collateral circulation and enhancing branch patency. Here we present the key principles of the hemodynamic flow modulation concept and its application in peripheral aneurysms as well as FIM cases for the treatment of thoracoabdominal aneurysms. The enrollment of a non randomized multi-center trial with the Cardiatis multilayer flow modulator, for thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm patients, with no alternative treatment, is currently being completed in France.
Mortality following surgical treatment of TAAA averages between 6% and 15% for elective procedures and between 50% to 60% for emergency operations 1-3. With 15% morbidity for elective procedures, complications are often major with significant risk of renal failure and respiratory insufficiency. This prolongs IC time. Paraplegia is the most feared and devastating complication and frequently leads to sphincter and posture problems. In all cases it is a severe invalidity and in France, since the law of 4th March 2002, leads to systematic claims for compensation before the CRCIs (regional medical accident compensation boards). To reduce these complications adjuvant therapies have been proposed: distal aortic perfusion by circulation bypass or passive shunt 4-6 profound general or local hypothermia with circulatory shutdown, drainage of the cephalorachidian fluid, re-attachment of the Adamkiewicz artery or intercostal arteries as well as postoperative surveillance 7, 8. In every interventional cardiovascular reference work, complete chapters are dedicated to this issue, and whole sessions are dedicated to this at international congresses.
The results of endovascular treatment for infrarenal and descending thoracic aortic aneurysms are now comparable with standard open surgical procedure. However, endovascular repair in the thoracoabdominal aorta has been limited due to the complexity of keeping visceral and renal arteries perfused. Attempts are being made to adapt endoluminal stent-grafts by using custom fenestrations and branched grafts. While preliminary data shows concept feasibility, these techniques are still investigational and require highlyskilled endovascular specialists and custom-made devices 7.
Should this device prove to be efficacious, this type of intervention could readily become more available to patients, due to the device’s ease of use and its ability to be used by more medical professionals (including vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists) than the treatment alternatives.
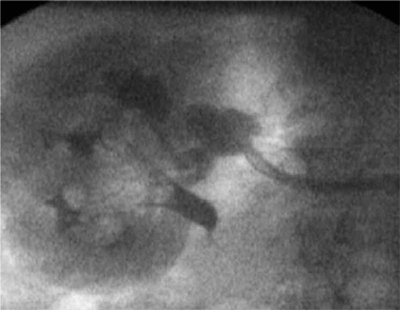
Fig. 74.2. – Branching renal aneurysms treated with Cardiatis Multilayer Flow Modulator.
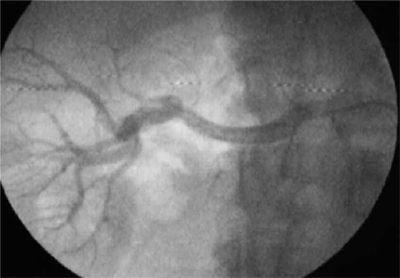
Fig. 74.3. – FU 6 months – exclusion of aneurysm and perfused collaterals and patent branches.
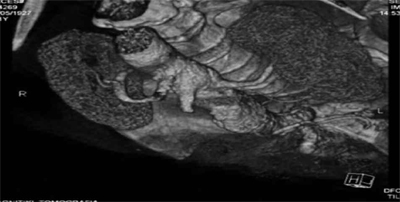
Fig. 74.4. – 30 month FU showing the 2 patent branches. Dr. Antonios Polydorou, Cardiologist, Evangelismos Hospital Athens. Greece.
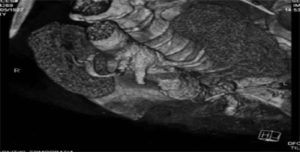
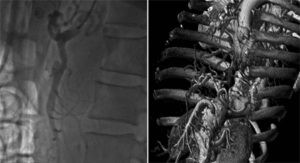
Fig. 74.5. – SM aneurysm treated with Cardiatis multilayer flow modulator, post implant and FU at 1Y. Dr. Sameer Dani, Cardiologist, Life care Institute of Medical Science & Research, Ahmedabad, India.
- 04. Patel HJ, Upchurch GR Jr, Eliason JL, Criado E, Rectenwald J, Williams DM, Deeb GM. Hybrid debranching with endovascular repair for thoracoabdominal aneurysms: a comparison with open repair. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;89(5):1475-81.
- 05. Ferrero E, Ferri M, Viazzo A, Gaggiano A, Maggio D, Berardi G, Piazza S, Cumbo P, Pecchio A, Lamorgese V. Hybrid open and endovascular repair of recurrent visceral aortic patch aneurysmal expansion after previous thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair: case report and description of technique. Minerva Chir 2010;65(3):393-400.
- 06. Biasi L, Ali T, Loosemore T, Morgan R, Loftus I, Thompson M. Hybrid repair of complex thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms using applied endovascular strategies combined with visceral and renal revascularization. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;138(6):1331-8.
- 07. Kieffer E, Chiche L, Godet G, Koskas F, Bahnini A, Bertrand M, Fléron MH, Goarin JP, Warnier de Wailly G, Benhamou AC. Type IV thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair: predictors of postoperative mortality, spinal cord injury, and acute intestinal ischemia. Ann Vasc Surg 2008;22(6): 822-8.
- 08. Chocron S, Vaislic C, Bonneville JF. Multilayer stents in the treatment of chronic type B dissection. Annals of thoracic surgery, in press.


